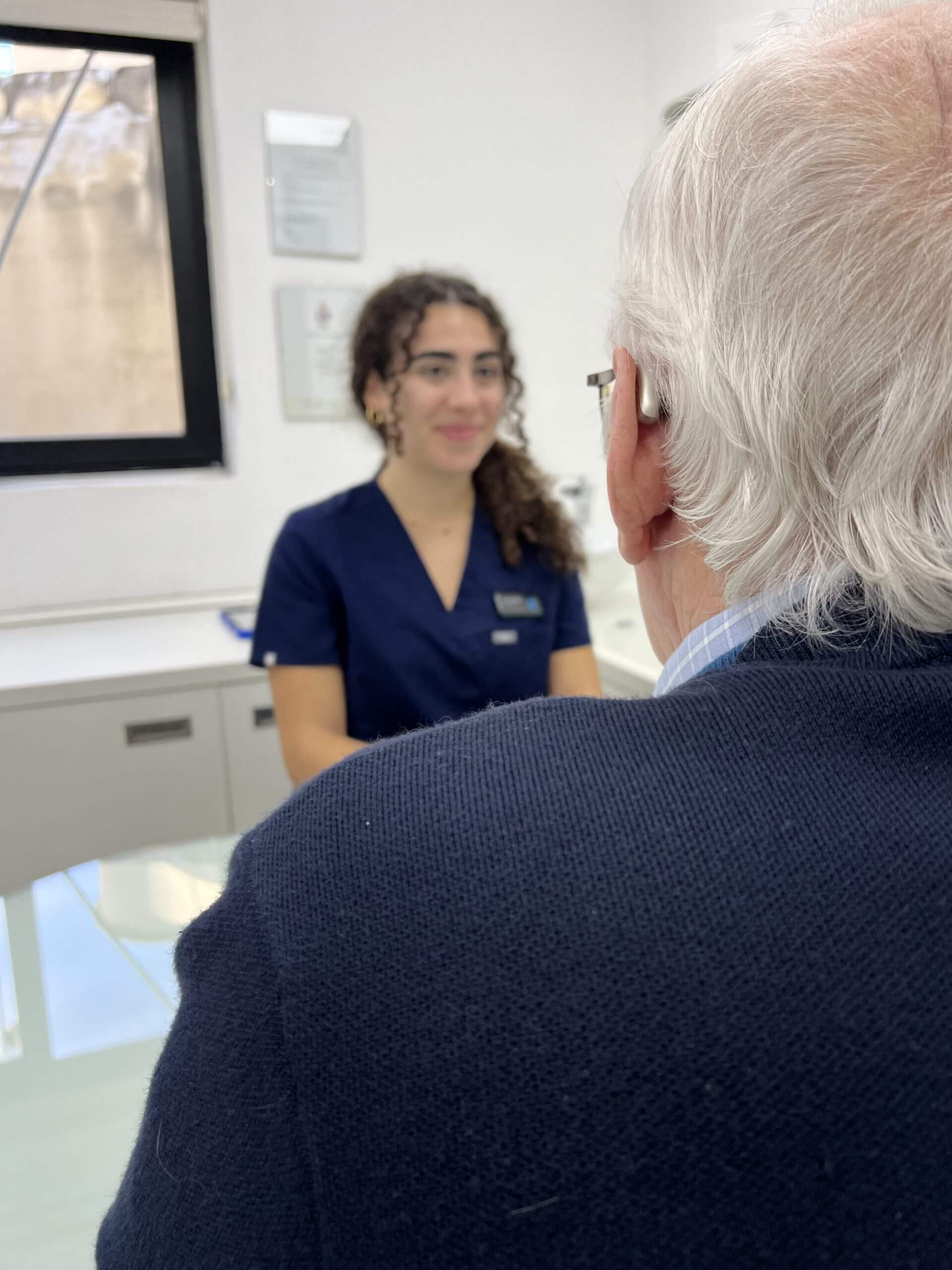

How to address your hearing loss
On average, it takes a person around 10 years to finally accept a hearing loss. That is not to say
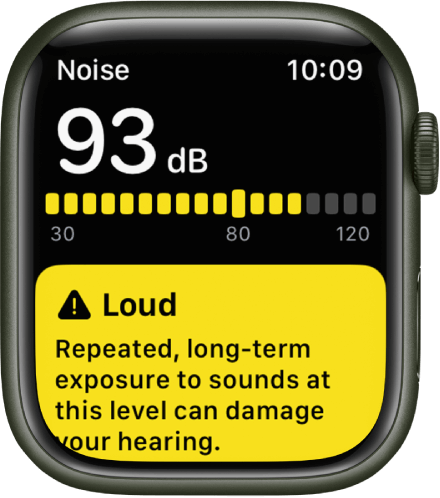
When discussing if headphones cause hearing loss, we must first look at how exposure to noise can damage your hearing. A prolonged exposure to very loud music and other recreational sounds can lead to noise-induced hearing loss. This is caused after exposure to loud noise over 85 decibels (dB) or more, for more than 8 hours. It can also be caused by a short-term exposure to sounds over 100 dB for as little as 15 minutes!
We are all guilty of coming across a song we love and cranking up the volume. Headphones aren’t regulated, meaning we can turn up the volume to the maximum for as long as we want. The scary thing is if you’re listening at this maximum level, your hearing could be damaged after just a few songs. Some smartphones have pop-up warnings when they detect that your volume is too high, so it’s really important that you pay attention to these.

When very loud music is heard, the hairs in the cochlear vibrate too intensely. When this happens, the hairs get overwhelmed and stop working properly. The good news is that, over time, it is possible for these hairs to recover. This is often the case after you’ve been at a music concert and temporarily struggle with your hearing. After a few hours, generally your hearing will return to normal. Sometimes, however, the hairs do not recover which is what we call a noise-induced hearing loss.
It’s a good idea to vary the way you listen to music each day. If you are at home and able to, we would suggest listening through a speaker or utilising your TV / computer. We understand that when exercising or travelling, headphones may be the only option. If this is the case, we would advise that you follow the 60/60 listening rule. This means limiting your listening of loud noise to 60 minutes per day and only go to 60% of the maximum volume. Following this rule will greatly help in reducing your risk of developing noise-induced hearing loss.
A lot of smart phones have settings that allow you to set a maximum volume for yourself. By doing this, you can ensure you never go over a safe listening level. All phones are different but if you go into the settings, there will be something about headphone safety levels. This is a great thing to have in place for when you are listening to music on the go. Some devices will even alert you if you are being exposed to an unsafe level of noise.
Public transport can be a noisy place and so it can be tempting to turn up the sound on your device. What you need to remember is that the background noise which is interrupting your listening experience is not reducing your volume, simply masking it. If you turn up your volume to counteract the background noise, you are making your listening experience even louder. If you plan to use headphones regularly in noisy settings, you should look at purchasing some noise-cancelling headphones. They can help to limit the background noise.
If you think you have caused damage to your hearing, you should consider booking yourself in for a hearing consultation. If you are concerned about noise-induced hearing loss and feel that you need some further advice, please just drop us a message.

On average, it takes a person around 10 years to finally accept a hearing loss. That is not to say
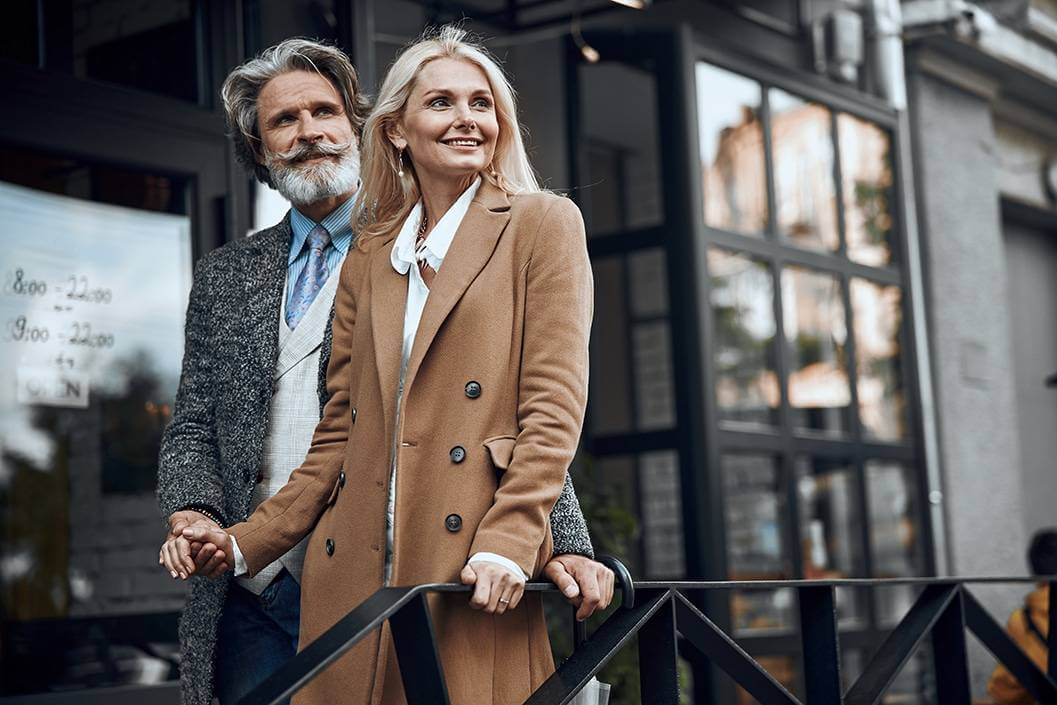

Living with a hearing loss does not just have to be a part of getting older. It can be treated
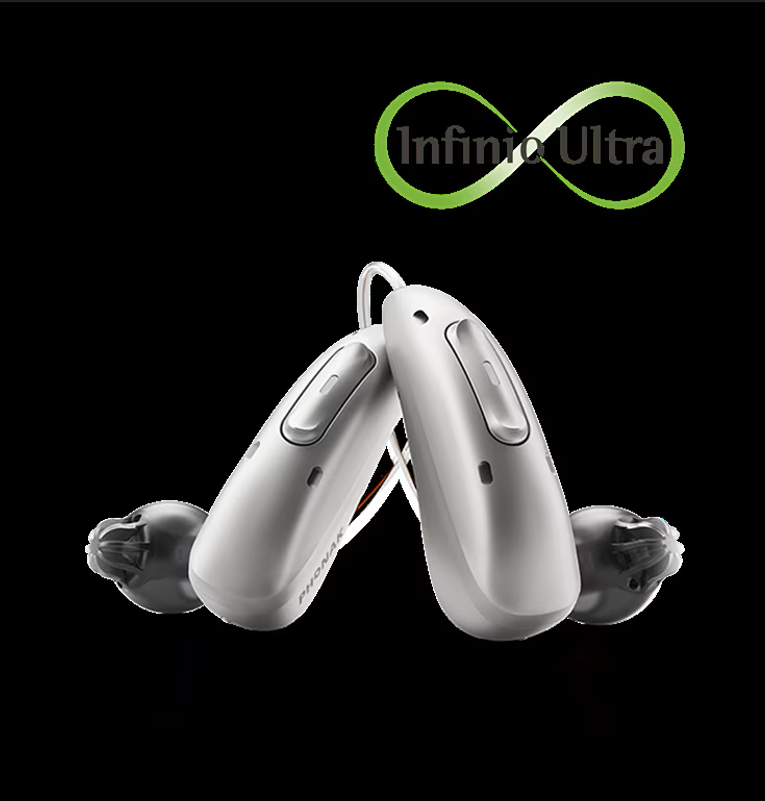

At the very end of 2024, Phonak released their brand new Infinio hearing aid technology. At the end of 2025,